Why is stainless steel melting point important for its mechanical properties

BlogDate: 26-04-2024 by: Ngan Le
In the manufacturing process, determining the stainless steel melting point plays a crucial role in predicting and analyzing the crystal structure and physical properties of the finished steel product thereafter. Identifying the ideal temperature for the melting process is a top concern for businesses when they need to identify suitable materials for their projects.
In today's article, let's explore the definition and significance of the melting point of stainless steel with MRS Steel. Additionally, we'll compare its melting point with other popular types of steel currently available in the market.

Determining the precise melting point of stainless steel is a necessary stage
Roles of stainless steel melting point to mechanical properties
Stainless steel is a special type of steel known for its high corrosion resistance, achieved through alloying with elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. During production, the stainless steel melting point is the specific temperature at which this type of steel transitions from a solid to a liquid state during heat processing. Determining the melting point of stainless steel is crucial for manufacturers as it directly influences the operations of melting and steel casting.
Specifically, the melting point of stainless steel is considered a prerequisite condition to ensure that the material does not undergo structural deformation during processing at high temperatures. Additionally, the melting point helps manufacturers identify the ideal temperature for subsequent casting, forging, or welding processes. However, after stainless steel has undergone hardening and preliminary processing steps such as rolling or forging, the melting point no longer holds significant importance for engineers or manufacturers.

The melting point help identify optimal temperature for subsequent manufacturing processes
The ideal temperature for grades of stainless steel melting point
Stainless steel is a type of alloy steel comprising multiple metal elements combined together, each of which typically has its own melting range. This leads to the stainless steel melting point often not falling within a fixed value; instead, it occurs within an expanded temperature range. Most alloying elements added to stainless steel often have higher melting points compared to iron, with chromium (Cr) specifically having a melting point of 1890°C while iron reaches 1535°C.

1375°C to 1450°C is the accurate temperature range for the stainless steel melting point
Therefore, for stainless steel, the melting point is usually higher than other types of steel due to the presence of chemical compounds such as chrome, nickel, and molybdenum. Typically, the stainless steel melting temperature can range from approximately 1375°C to 1450°C, depending on the specific composition of each type of stainless steel. Its stability and excellent heat resistance are crucial factors that make it suitable for a wide range of high-intensity applications.
Table of melting temp of stainless steel grades
Stainless steel is a special type of steel with various grades ranging from austenitic stainless steel (such as 304, 316, and 317) to ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel (410 and 420),... All of these steel grades have different thermal expansion coefficients and melting points due to differences in chemical composition and mechanical properties of stainless steel. Below is a table listing the melting points of various types of stainless steel:
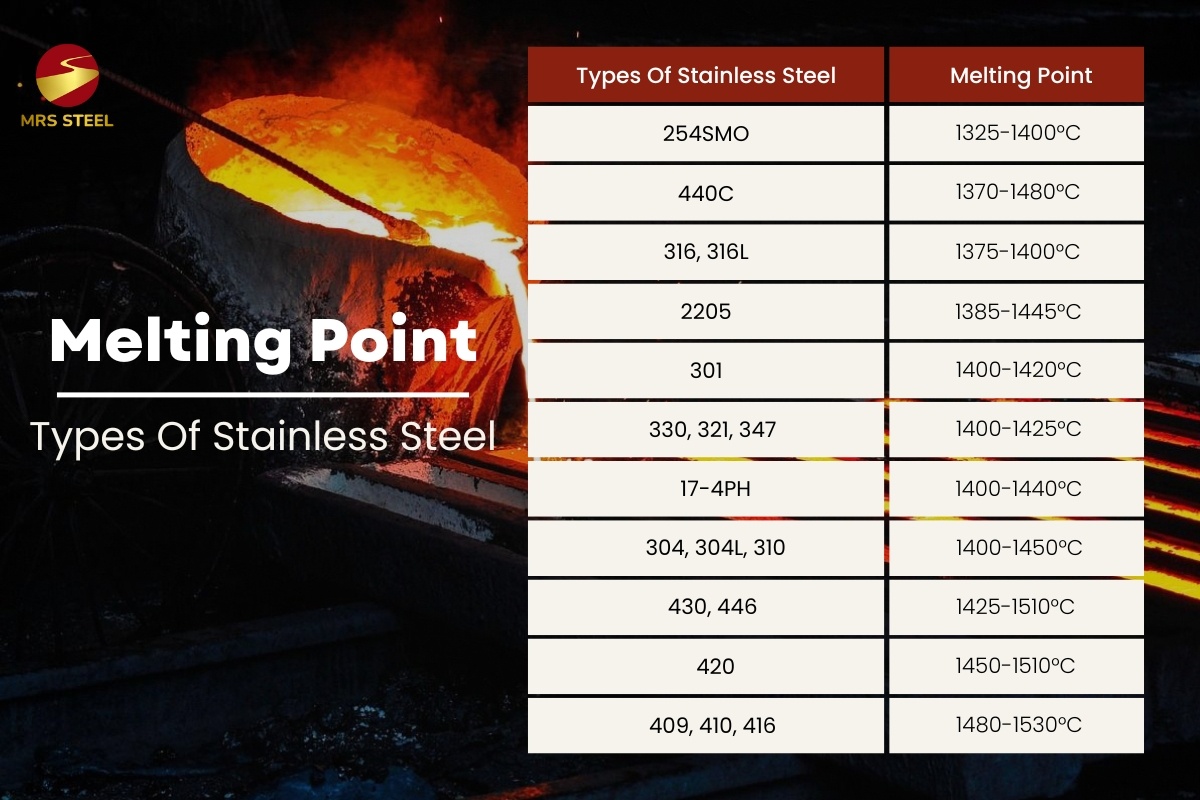 The melting points of steel types and other metals
The melting points of steel types and other metals
List of factors affect the melting temp of stainless steel
At high temperatures, many materials, including stainless steel, begin to significantly reduce their tensile strength and hardness even before reaching the melting point. A typical case with stainless steel, this material can retain 100% structural integrity at 870°C (1679°F), but at 1000°C (1832°F), it loses 50% of its tensile strength.
Exposure to high temperatures not only makes stainless steel prone to deformation but also affects the protective oxide layer of stainless steel, increasing the risk of corrosion and rusting in the future. In summary, during the heating process, even if the stainless steel melting point has not been accurately reached, it can still be damaged when exposed to high temperatures. Therefore, fabricators need to regularly monitor and control the stainless steel melting temperature to ensure structural integrity.

High temperatures and amount of impurities in the structure directly affect to stainless steel melting point
In steel composition, elements other than the main constituents (iron and carbon) are considered an impurity, and the amount of impurities directly affects the melting rate of the steel. Stainless steel, with the presence of various impurities such as nickel, chromium, and molybdenum, tends to have a slower melting rate compared to other types of steel. Therefore, the stainless steel melting point can vary depending on the amount of impurities in the structure; the melting point increases as the amount of impurities decreases and vice versa.
The difference between melting point of stainless steel 304 & 316
304 and 316 are the two most common types of stainless steel in today's industry. Both originate from Austenitic stainless steel with a face-centered cubic crystal structure. This structure is considered unique as it remains unchanged at all temperatures from freezing to the precise stainless steel melting point. Although both types of steel share the same crystal structure, their chemical compositions differ, particularly in the amounts of nickel, molybdenum, and other elements.
The melting point of stainless 304 is 1400°C while 316 is approximately 1375°C
The melting points of stainless steel 304 and 316 have slight differences.The melting point of stainless steel 304 is around 1400-1450°C (2552-2642°F), while the range of stainless steel melting temperature 316 is approximately 1375-1400°C (2507-2552°F). The difference in chemical composition and melting point between stainless steel 304 and 316 makes each type suitable for distinct applications.
Finding cost-effective options for stainless steel at MRS Steel
Understanding the precise stainless steel melting point plays a crucial role in enabling manufacturers to carry out machining operations such as casting, forging, or rolling smoothly thereafter. Failure to control and monitor temperatures regularly during heat treatment can adversely affect the crystal structure, thereby reducing the quality of the final output of stainless steel products.
Therefore, selecting reputable factories for stainless steel production is essential if you are in need of purchasing this product for your project. MRS Steel, as a specialized provider of steel solutions for importers, will help you save time and effort in selecting a quality stainless steel supplier. We not only possess extensive knowledge of the steel market and industry but also have relationships and connections with leading steel factories in Vietnam.

Cooperating an unit which have good relationships with large mills will optimize time and cost for importers
For any questions about stainless steel melting point or inquiries regarding stainless steel products, including sizes or price lists, please contact MRS Steel via Whatsapp: +84 76 911 2358 or email vanloc@mrssteel.com.vn for free consultation!






















































