Red Sea War: Concerns for International Transportation

Steel NewsDate: 28-12-2023 by: Nhu Quynh
A new crisis is brewing in the Red Sea, one of the world's vital trade routes, with the potential to disrupt supply chains and drive up oil prices and inflation. This comes at a time when economic growth is slowing down.
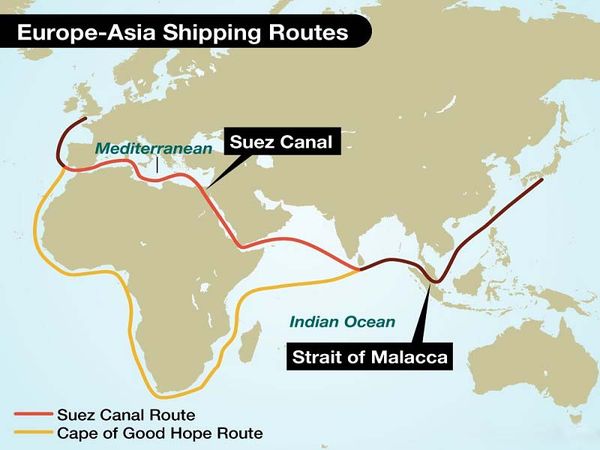
Red Sea - Important Maritime Transportation
As one of the crucial maritime routes, it accounts for approximately 15% of global maritime transportation volume. The Red Sea shows no signs of easing tensions, especially as recent Houthi warnings indicate a potential expansion of their targets in the region if the United States launches a campaign against their forces.
The mentioned developments come shortly after Washington announced the formation of a coalition comprising various countries, including the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain,... to address Houthi attacks on shipping in the Red Sea. Simultaneously, this coalition has deployed military assets to counter missile and drone attacks.

Conflict in the Red Sea and the Risk of an International Transportation Crisis
The Suez Canal is currently the shortest maritime route connecting Asia and Europe, accounting for approximately 15% of global maritime traffic. The conflict in the Red Sea has a significant impact on the global transportation and trade situation. This route is closely linked to the Suez Canal, meaning that ships avoiding the Red Sea also have to steer clear of the crucial route through the Suez Canal. This canal is one of the seven critical chokepoints for global transportation.
The drone and missile attacks by Houthi forces in Yemen on vessels navigating the Red Sea are forcing global shippers to reroute their journeys around the Cape of Good Hope in Southern Africa. This redirection extends the sea travel time by an additional 10–14 days. The harsh weather and frequent rough seas at the Cape of Good Hope and the Mozambique Channel result in faster fuel consumption, leading to increased fuel costs. Additionally, vessels face numerous challenges, including fuel replenishment, cargo restocking, customs issues, overloading and inadequate infrastructure at African ports.
These wars are creating a significant risk of disruption to transportation activities through the Suez Canal and the Red Sea, leading to increased shipping costs for various types of vessels, including tankers, container ships, and bulk carriers, thereby indirectly supporting the recovery of oil prices. Additionally, ships passing through the Red Sea are facing significantly higher conflict-risk insurance premiums, with current fees having surged by fivefold. Meanwhile, many transportation experts believe that disruptions in routes may lead to a situation where ships are in the wrong position and containers are misplaced, resulting in port congestion.
In the face of the complex developments in the Red Sea and economic risks, the United States, the European Union (EU), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and several countries, including Yemen, have issued a joint statement condemning Houthi interference in maritime rights and freedoms.
If the “Red Sea crisis” persists for only a short period, consumers may not notice much, except for possibly higher energy prices. However, if the situation prolongs, it not only affects maritime transportation but also poses a risk of uncontrollable inflation impacting the world.